1 Answer1 You are right since the vertex is above the focus, the parabola must open downwards So p = − 10 and the parabola has equation ( x − 1) 2 = − 40 ( y − 2) Note that the right hand side is never negative because for all points on the parabola y ≤ 2 (because the parabola opens downwards)Start studying Parabola (xh)^2=4p(yk) Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools6 Which shape is defined by the equation y 2 = 12x?

For The Equation Of The Parabola Given In The Form Chegg Com
If the focus of the parabola (y-k)^2=4(x-h)
If the focus of the parabola (y-k)^2=4(x-h)- If a parabola has a vertical axis, the standard form of the equation of the parabola is (x – h) 2 = 4p(y – k), where p≠ 0 The vertex of this parabola is at ( h , k )Answer The Focus is located within the curve of the parabola



Conic Sections And A New Look At Parabolas Ppt Download
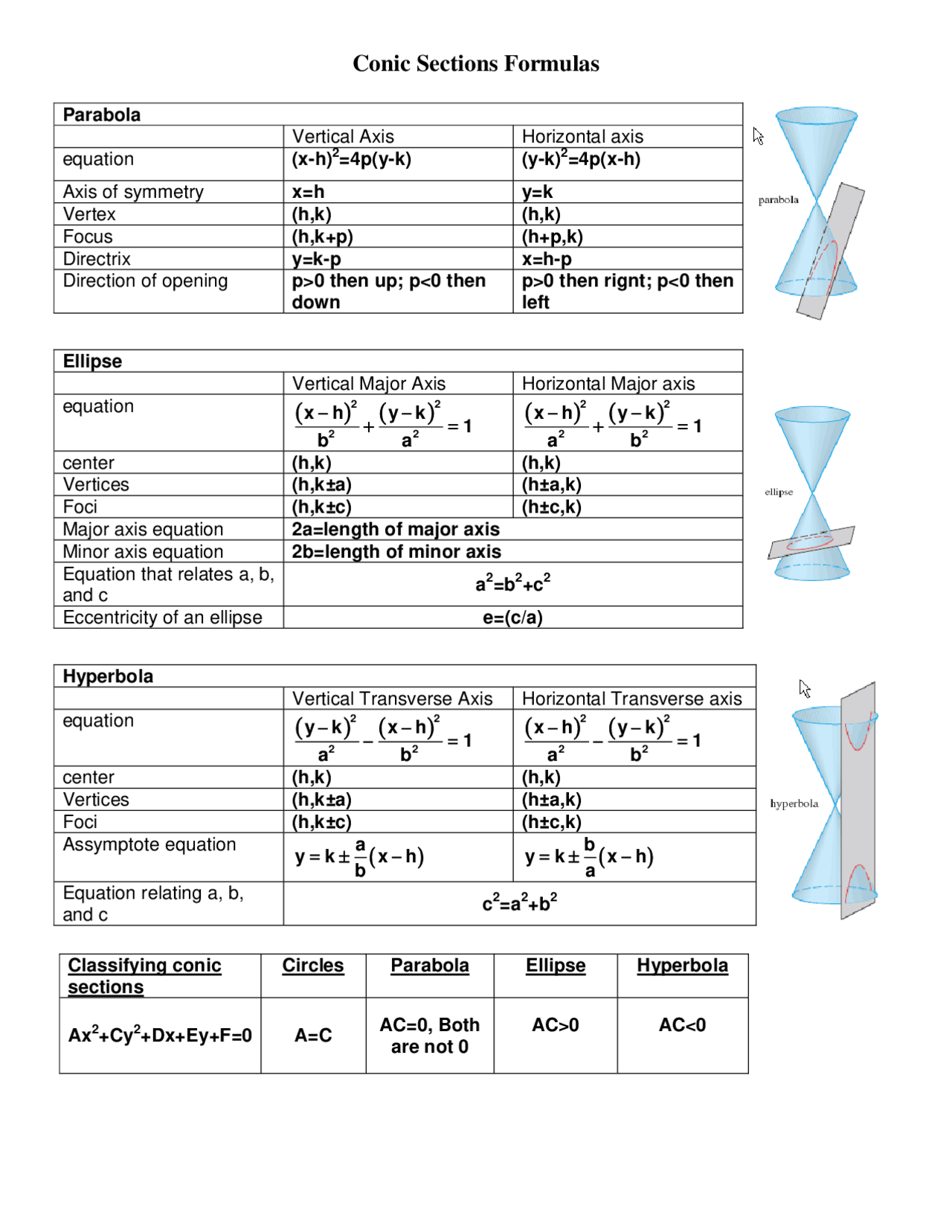
• Given the focus and directrix of a parabola, or the focus and vertex, or the vertex and directrix, write down its equation in the form (xh)2 = 4p(yk) or (yk)2 = 4p(xh) • Graph a parabola given in the form (x h)2 = 4p(y k) or (y k)2 = 4p(x h) and locate its focus, directrix, and axis of symmetryView this answer If the given equation is (x−h)2 = 4p(y−k) ( x − h) 2 = 4 p ( y − k) , then the parabola has a vertical axis The equation can be rewritten as {eq}\dfrac {1} {4p} (x$$ Parabola (xh)^2=4p(yk) $$ $$ Vertex (h, k) , Focus (h, kp) $$ h k p Add Parabola Ellipse $$ Ellipse (xh)^2/a^2(yk)^2/b^2=1 $$ Center (h, k) Length of major axis is 2a Length of minor axis is 2b h k a b Add Ellipse Hyperbola
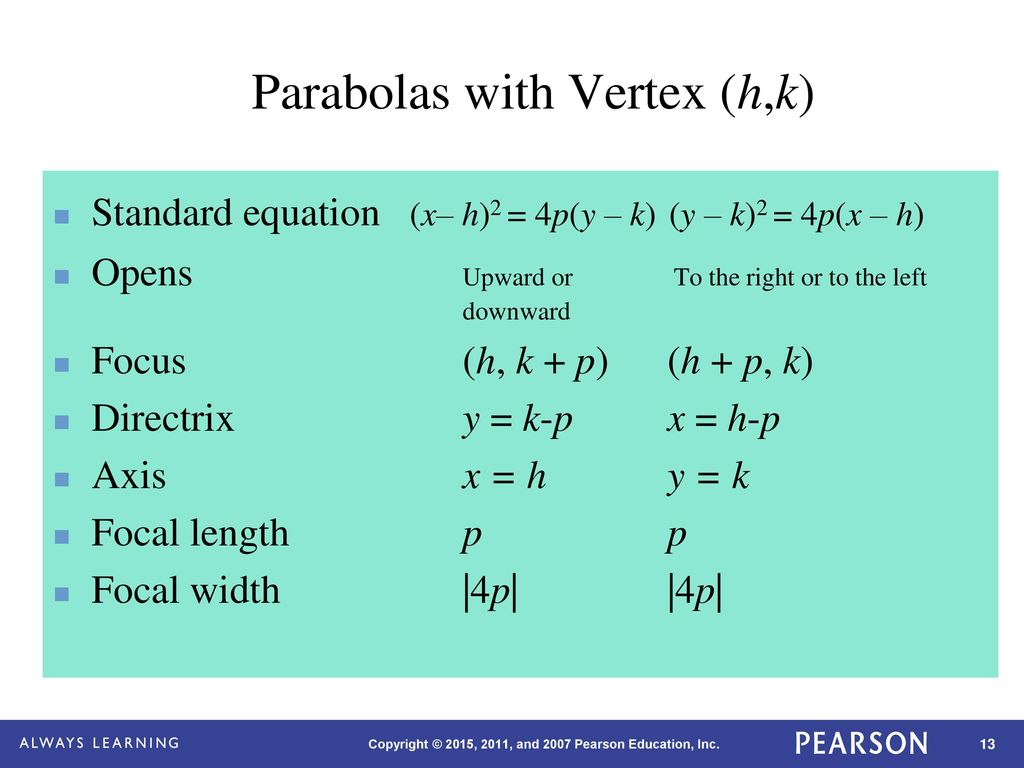
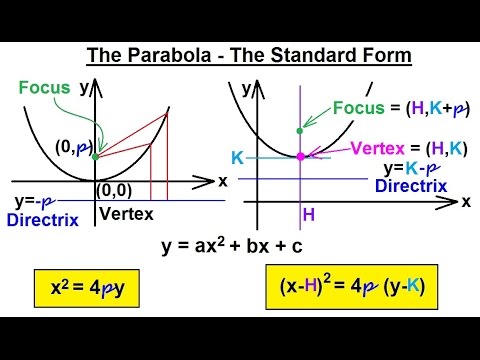
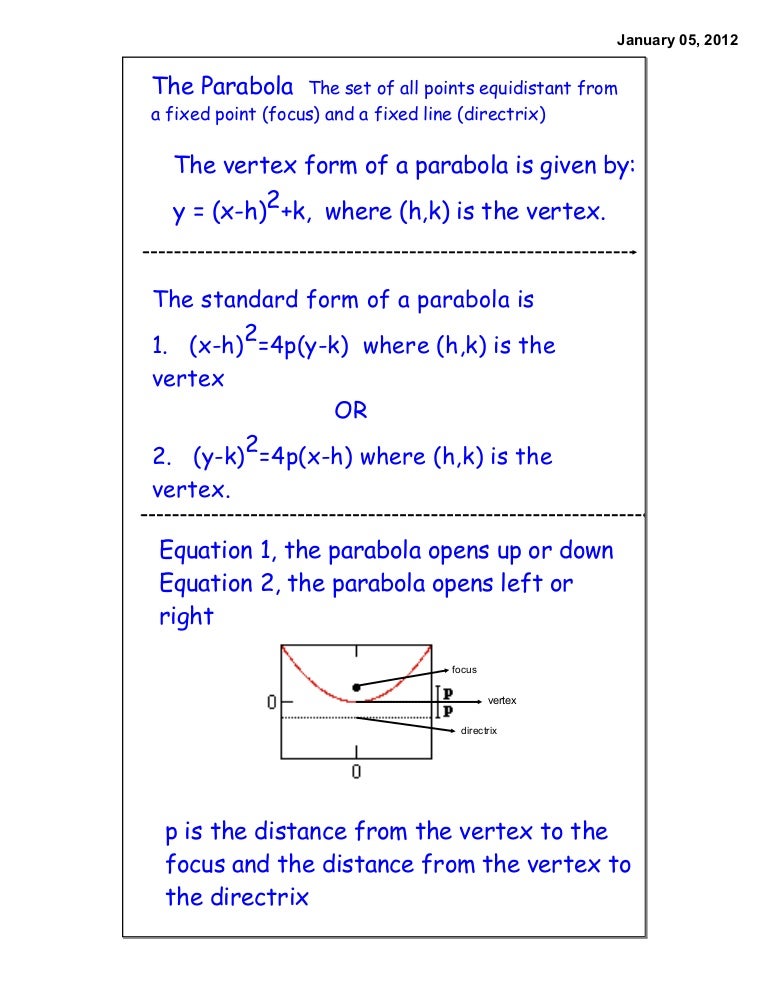
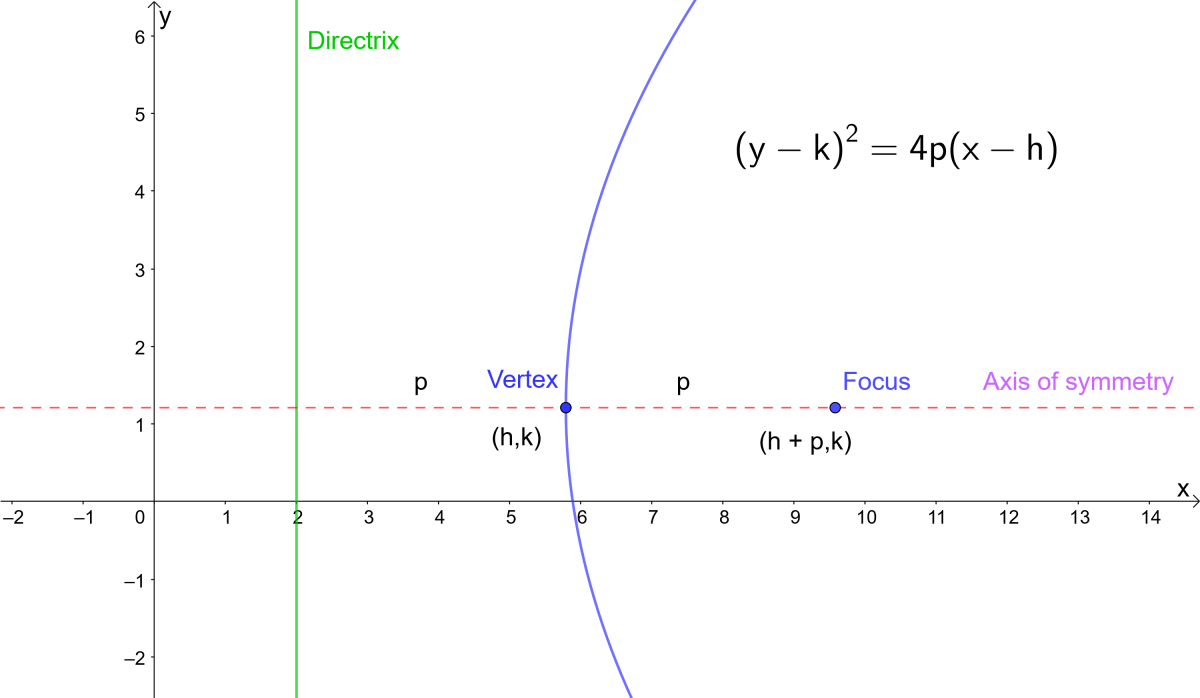
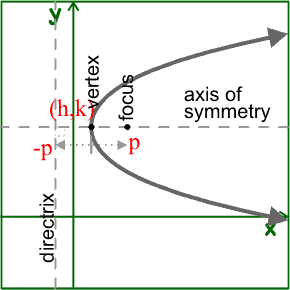
For parabolas that open sideways, the standard form equation is (y k)^2 = 4p(x h) The vertex or tip of our parabola is given by the point (h, k) For parabolas that open up and down, the focus point is given by (h, k p) For parabolas that The standard form is (x – h)2 = 4p (y – k), where the focus is (h, k p) and the directrix is y = k – p If the parabola is rotated so that its vertex is (h,k) and its axis of symmetry is parallel to the xaxis, it has an equation of (y – k)2 = 4p (x – h), where the focus is (h p, k) and the directrix is x = h – pFor this kind of parabola, the attention is centered at the point (h, k p) and the directrix is a lineup located at y = k p On the flip side, the equation of a parabola calculator with a vertex at (h, k) and a horizontal axis of symmetry is described as (y k)^2 = 4p(x h)
The standard form is (x h) 2 = 4p (y k), where the focus is (h, k p) and the directrix is y = k p If the parabola is rotated so that its vertex is (h,k) and its axis of symmetry is parallel to the xaxis, it has an equation of (y k) 2 = 4p (x h), where the focus is (h p, k) and the directrix is x = h pParabola Vertical Axis Horizontal axis equation (xh)2=4p(yk) (yk)2=4p(xh) Axis of symmetry x=h y=k Vertex (h,k) (h,k) Focus (h,kp) (hp,k) Directrix y=kp x=hp Direction of opening p>0 then up;Ecuacion de la parabola con vertice fuera del origen en eje focal paralelo y , ( x h )^2 = 4p( y k )




Como Pasar De La Ecuacion General A La Ecuacion Canonica En La Parabola Youtube



Parabola Equations And Graphs Directrix And Focus And How To Find Roots Of Quadratic Equations Owlcation
500 write the equation for a center of (2,4) what is x^2 4x y^2 8y = 2?A parabola is formed by an equation in the form (y – k) 2 = 4p(x – h) (This is the standard form of a parabola) Answer Parabola 7 The graph is an ellipse, which can be written in the form (x – h) 2 a 2 (y – k) 2 b 2 = 1 The center of the ellipse is at the point (2, 3) The value of a is 6 since the vertices are at the points (2Standard form of parabola equation is, (X h)^2 = 4p(Y k) Given equation can be written as (X 0)^2 = 6(Y 0) So the vertex of this parabola is at origin (0,0) 4p = 6 => p = 6/4 = 3/2 F = (h,kp) => F = (0,3/2) Directrix is at Y = X p => Y



1



2
If a parabola has a horizontal axis, the standard form of the equation of the parabola is this (y k)2 = 4p(x h), where p≠ 0 The vertex of this parabola is at (h, k) The focus is at (h p, k) The directrix is the line x = h pThen graph the parabola The equation is in standard form and the squared term is x, which means that the parabola opens vertically Because 4p = 12, p = 3 and the graph opens upward The equation is in the form (x — h)2 = 4p (y — k) , so h = 3 and k = —4 Use the values of h, k, and p to determine the characteristics of the parabolaThis is a topic level video of Graphing a Parabola of the Form y = a(xh)^2 k for the ASU College Algebra and Problem Solving CourseJoin us!https//wwwed




More Conic Sections Objective Given A Translation I Can Graph An Equation For A Conic Section Ppt Download



Parabola Definition And Equation
For parabolas that open either up or down, the standard form equation is (x h)^2 = 4p(y k) For parabolas that open sideways, the standard form equation is (y k)^2 = 4p(x h) The vertex or tip of our parabola is given by the point (h, k)Given a standard form equation for a parabola centered at (h, k), sketch the graph Determine which of the standard forms applies to the given equationlatex\,{\left(yk\right)}^{2}=4p\left(xh\right)\,/latexorlatex\,{\left(xh\right)}^{2}=4p\left(yk\right)/latexVertex V = (2,1), Focus F = (2,0) X coordinate 2 is common, so parabola is vertical and focus is above vertex, so it opens upwards Distance p between vertex and focus is (0(1) 1 unit, so length of focal chord or latus rectum is 4p, 4 units St



Precalculus Algebra Review Conic Sections 5 Of 27 The Parabola Standard Form Youtube
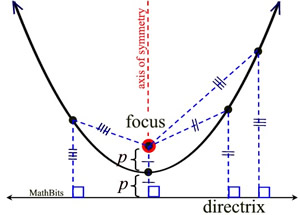



Parabola Equations Mathbitsnotebook Geo Ccss Math
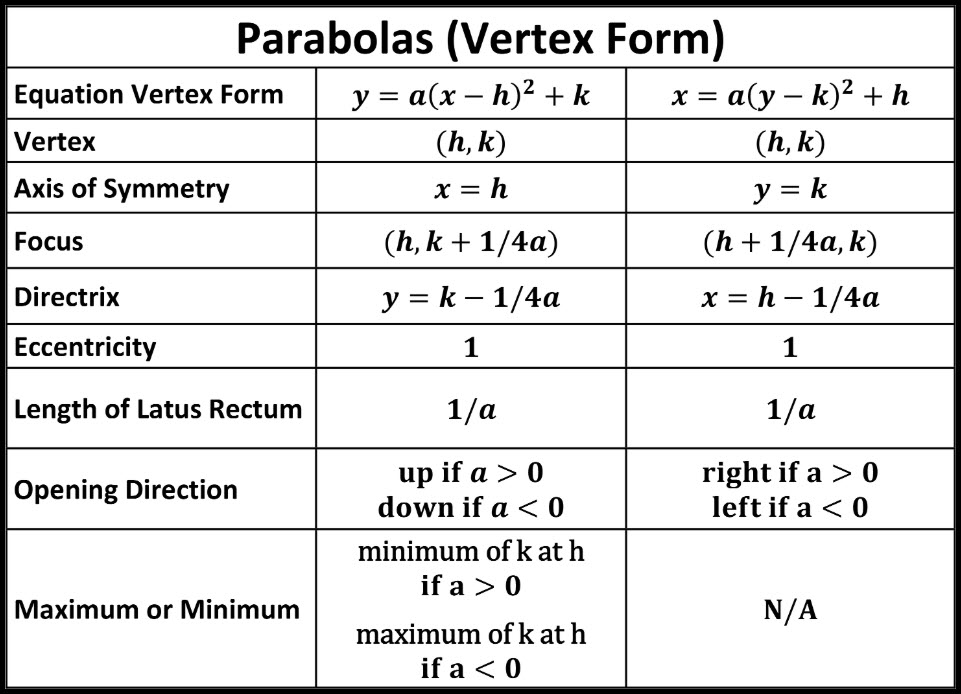
0 find the focus of the parabola x^2=22y what is (0,11/2)?\({\text{Parabolas (Alternative Vertex Form)}}\) \({\text{Equation Vertex Form}}\) \((xh)^2=4p(yk)\) \((yk)^2=4p(xh)\) \({\text{Focus}}\) \((h,kp)\) \((hp,k)\) \({\text{Directrix}}\) \(y=kp\) \(x=hp\) \({\text{Opening Direction}}\) \(\text{up if } p\gt0, \text{ down if } p \lt 0\) Standard form of parabola (yk)^2=4p(xh), with (h,k) being the (x,y) coordinates of the vertex This parabola opens leftwards and has a horizontal axis of symmetry Which is the focus of a parabola with equation mc003 1 JPG?
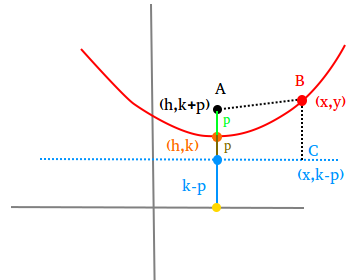



Parabola Definition And Equation
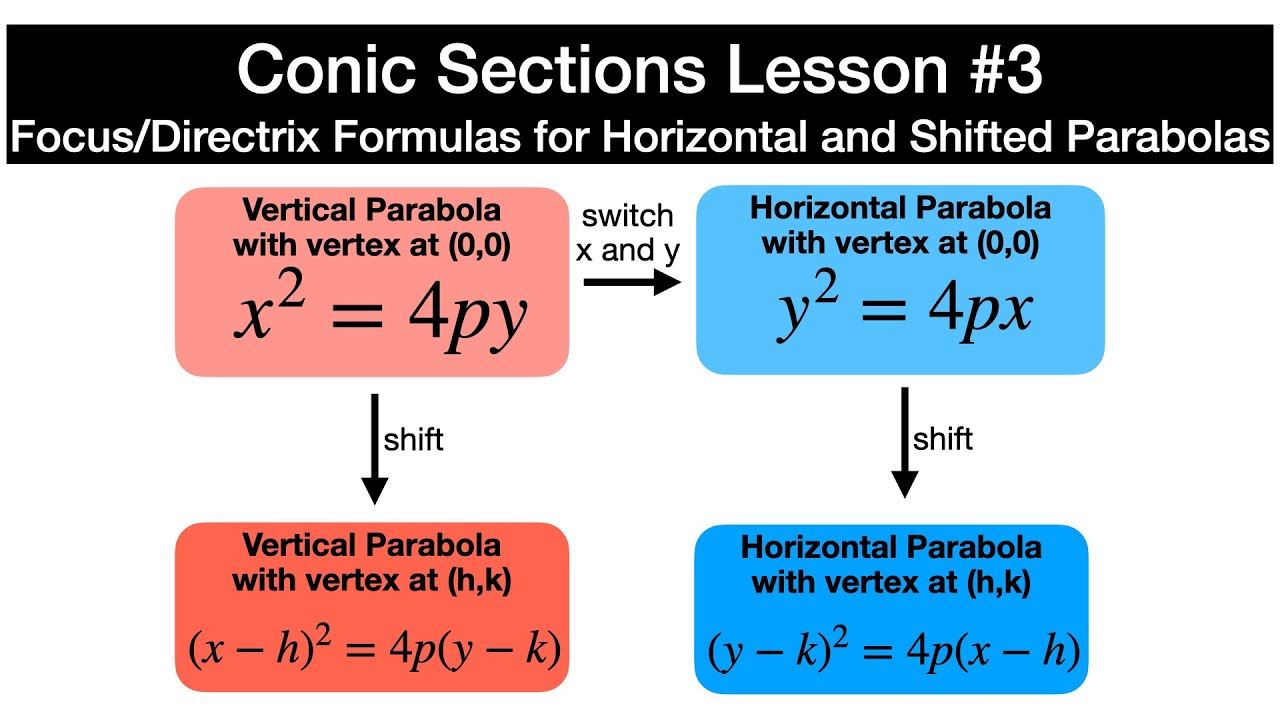



Shifted And Horizontal Parabolas Precalculus Conic Sections Lesson 3 Youtube
(y k) 2 = 4p ( x h) the vertex is midway between the focus and the directrix so it must be (1, 8) So far the equation must look like this (y 8) 2 = 4p ( x 1) the distance between the vertex and the focus is 3 units so p = 3 Since the parabola opensNote • (x h)2 = 4p (y k) Parabola open up (U) if p>0 and opend down (D) if p0 and opend to the left (L) if pThe standard form is (x h)^2 = 4p (y k), where the focus is (h, k p) and the directrix is y = k p If the parabola is rotated so that its vertex is (h,k) and its axis of symmetry is parallel to the xaxis, it has an equation of (y k)^2 = 4p (x h), where the focus is (h p, k) and the directrix is x = h p (xh)^2 = 4p(yk) Vertex




Parabola Transporte En El Peru



Conic Sections Parabolas Summary Analysis Sparknotes
400 Identify which of the two equations is a circle a) (x9)^2 (y2)^2 = 49 b) 25x^2 4y^2 =100 The circle is equation a Because when we divide the 49 out, each fraction will have the same denominator whereas in equation b, when we divide the 100 out, each fraction will have a different denominatorFor the equation of the parabola given in the form (y k)2 = 4p(xh), (a) Identify the vertex, value of p, focus, and focal diameter of the parabola (b) Identify the endpoints of the latus rectum (c) Graph the parabola (d) Write equations for the directrix and axis of symmetry Express numbers in exact, simplest form (y4)² = 16(x4)Whereas the directrix is \( y = k – p \) If we rotate the parabola, then its vertex is \( (h,k) \) However, the axis of symmetry is parallel to the xaxis, and its equation will be \( (y – k)2 = 4p (x – h)\) , Now the focus is \( (h p, k)\) The directrix of parabola is \( x = h – p \)
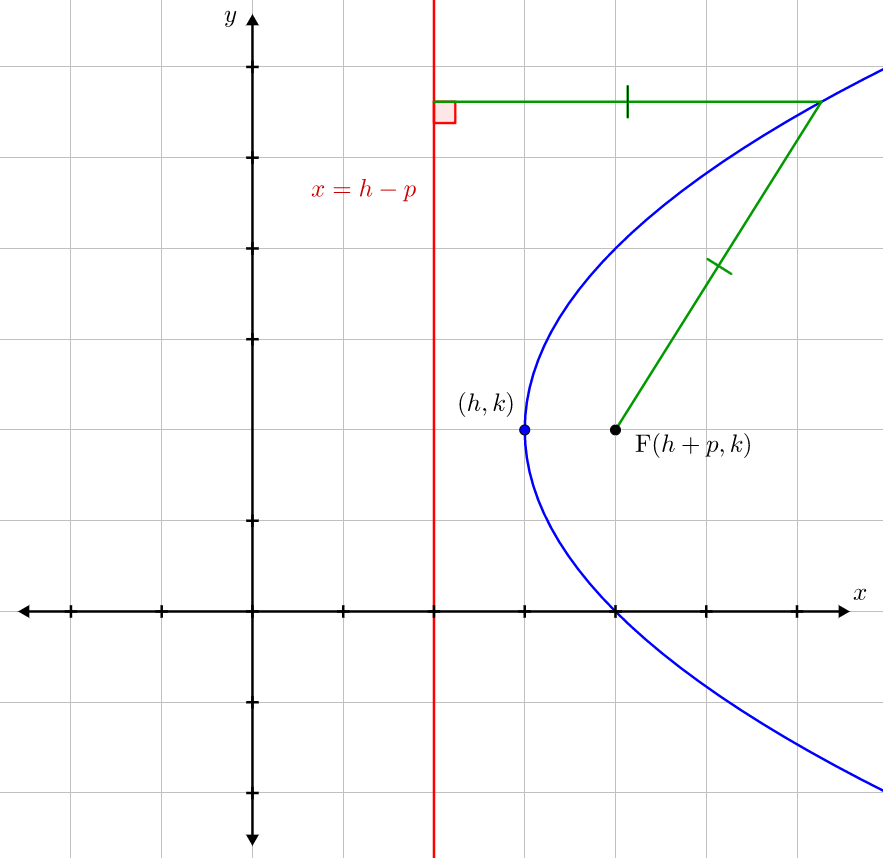



Conic Sections Brilliant Math Science Wiki




Chapter 8 1 Conic Sections Parabolas Honors Pre Calculus Rogers High School Pdf Free Download
100 the circle equation what is (xh)^2(yk)^2=r^2?When p is positive, the parabola opens upward When p is negative, the parabola opens downward (x h)2 = 4p(y k) The Standard Form of the Equation with Vertex (h, k) For a parabola with an axis of symmetry parallel to the xaxis and a vertex at (h, k), the standard form is The equation of the axis of symmetry is y = kParabola is a plane curve which is mirrorsymmetrical and is approximately Ushaped I put a picture of a teapot, because there are two Ushaped elements, which is the spout and handle of the teapot Other examples of parabola could be a jumping dolphin and a bridge The formula is (y k)^2 = 4p(x h) and (x h)^2 = 4p(y k)




8 2 Graph And Write Equations Of Parabolas Analytic Geometry Geometry
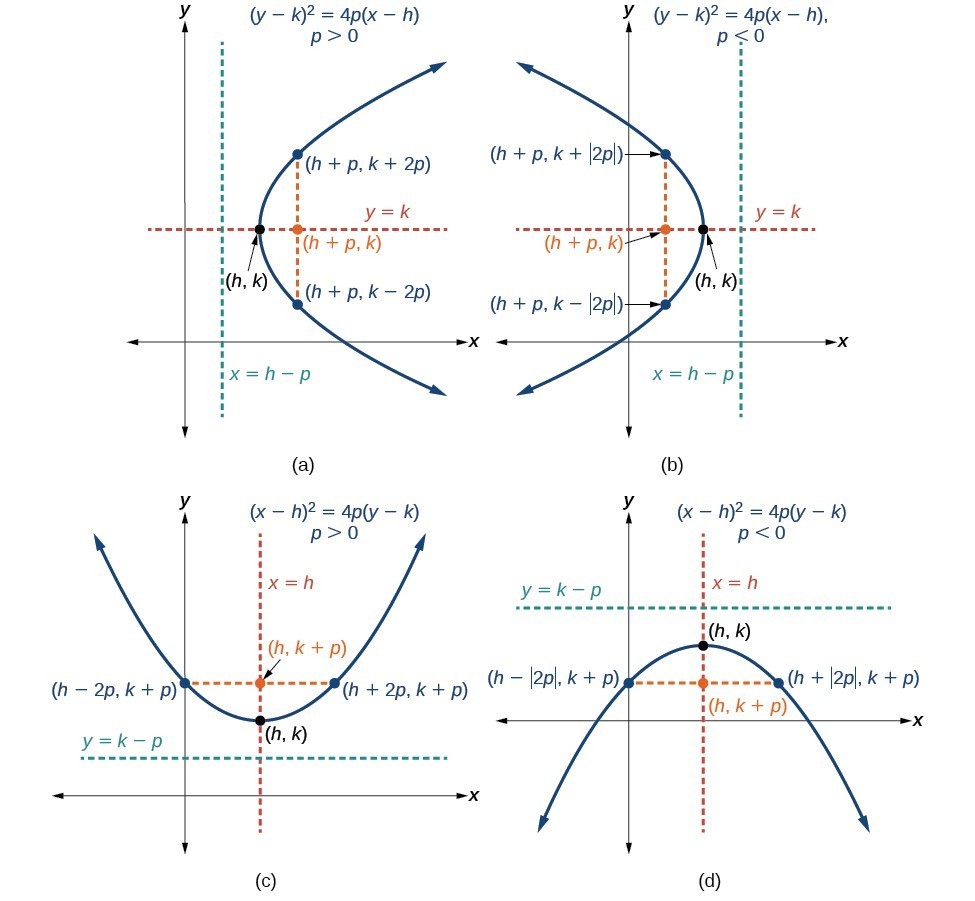



Parabolas With Vertices Not At The Origin College Algebra
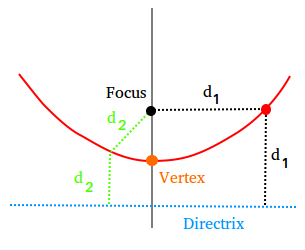
The standard form is (x h) 2 = 4p (y k), where the focus is (h, k p) and the directrix is y = k p If the parabola is rotated so that its vertex is (h,k) and its axis of symmetry is parallel to the xaxis, it has an equation of (y k) 2 = 4p (x h), where the focus is (h p, k) and the directrix is x = h pThe equation (x h) 2 = 4p(y k) above applies when the parabola opens upward or downward with a directrix of y = kp If the parabola opens to the right or to the left with a directrix of x = hp, the equation to use is (y k) 2 = 4p(x h)PARABOLA Definition A parabola is the collection of all points in the plane that are the same distance from a fixed point, called the focus (F), as they are from a fixed line, called the directrix (D) Standard Form (x h) 2 = 4p(y k) (y k) 2 = 4p(x h) p > 0 Parabola opens UP p > 0 Parabola opens RIGHT p < 0 Parabola opens DOWN p < 0




Parabola Conic Section Warmup Graph The Following Parabola




Conic Sections And A New Look At Parabolas Ppt Download
This means that the parabola opens to the left, and consequently, its standard form is $(y –k)^2 = 4p(x – h)$, where $p$ is negative Since the distance of the vertex from the directrix is $3$ and knowing that $p$ must be negative, $p = 3$Level S Units 2532 Mandarin Chinese Vocabular 52 Terms See all 5 sets in this study guide 5 Terms msaba11 Parabola (xh)^2=4p (yk) Vertex Axis of Symmetry DirectrixThe standard form is (x h)2= 4p (y k), where the focusis (h, k p) and the directrix is y = k p If the parabola is rotatedso that its vertex is (h,k) and its axis of symmetry is parallel to thexaxis, it has an equation of (y k)2= 4p (x h), where thefocus is (h p, k) and the directrix is x = h p




Focus Directrix Of A Parabola From Equation Video Khan Academy




More Conic Sections Objective Given A Translation I Can Graph An Equation For A Conic Section Ppt Download
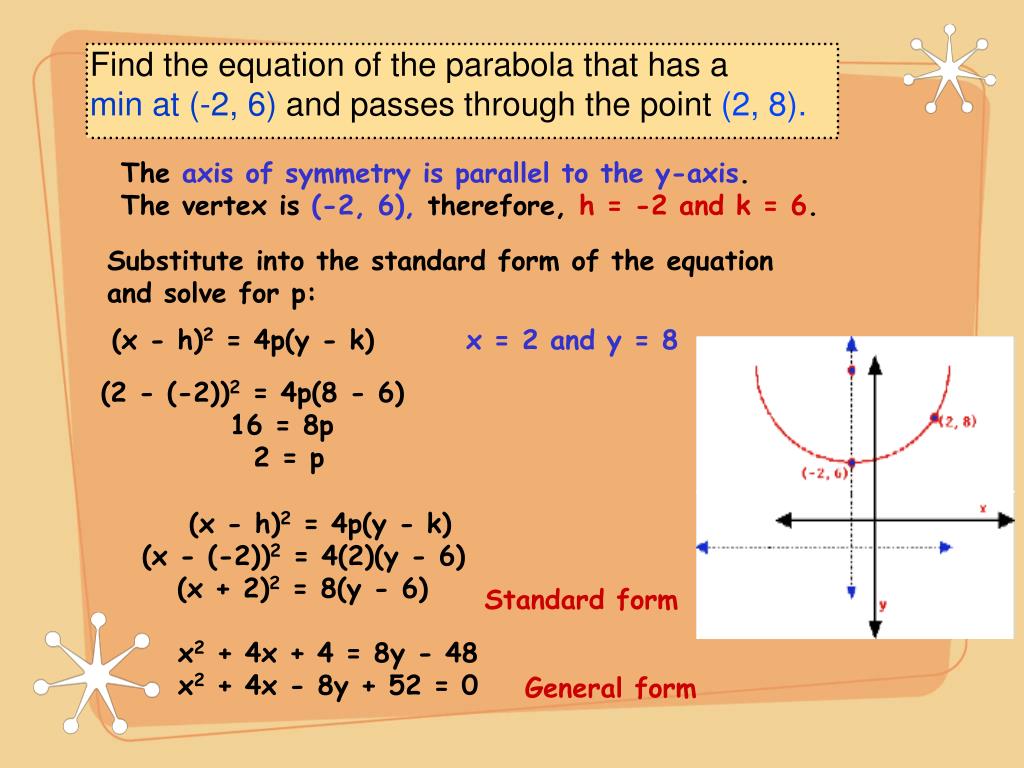
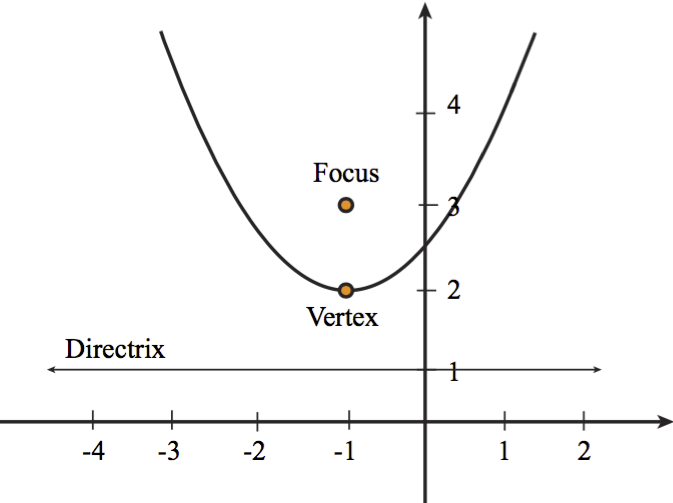
To graph parabolas with a vertex \((h,k)\) other than the origin, we use the standard form \({(y−k)}^2=4p(x−h)\) for parabolas that have an axis of symmetry parallel to the \(x\)axis, and \({(x−h)}^2=4p(y−k)\) for parabolas that have an axis of symmetry parallel to the \(y\)axisF = (h,k p) and the equation of the parabola is y = 1/4p (x h) 2 k Note that vertex will always be half way between the focus and the directrix Example Find the equation of the parabola with Focus at (1,2) and directrix y = 4 Solution Here the equation is horizontal parabola standard form (y k) 2 = 4p(x h) If given the directrix is y = 6 then directrix y = k p , so here 4p is distiributed for (x h) Here the equation is vertical parabola standard form(x h) 2 = 4p(y k) answered by david Expert




3 A Find An Equation Of The Parabola X H Chegg Com



Http Home Miracosta Edu Dbonds Math 155 lecture notes section 10 1 Pdf
PARABOLA (y k) 2 4p (x h) Opens left or right Focus (h p, k) Directrix x h p 5 PARABOLA (x h) 2 4p (y k) Opens up or down Focus (h, k p) Directrix y k p 6 Write an equation of the parabola whose vertex is at (2, 1) and whose focus is at (3, 1) SOLUTION Find h and k The vertex is at (2, 1), so h 2 and k 1 (y 1) 2 4p(x 2) 7 Write an equation of the parabola whose vertex isGiven {eq}(x h)^2 = 4p(y k), {/eq} the ordered pairs representing the vertex and focus are _____ and _____, respectively The directrix is the line defined by the For a horizontal parabola, focus = (hp,k) ∴ (hp,k) = (3,2) ⇒hp = 3 and k= 2 For a horizontal parabola the equation of directrix is x = h−p ∴ h−p =−1 Solving the equations hp =3 and h−p = −1, we get h = 1 and p = 2 ∴ vertex =(1,2) equation of parabola(y−k)2 = 4p(x−h) ⇒(y−2)2 = 8(x−1)2




Parabola Focus Directrix Review Article Khan Academy
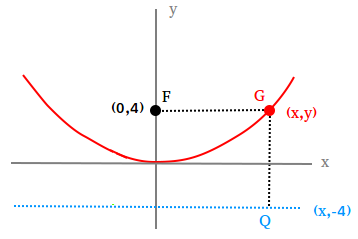



Parabola Definition And Equation
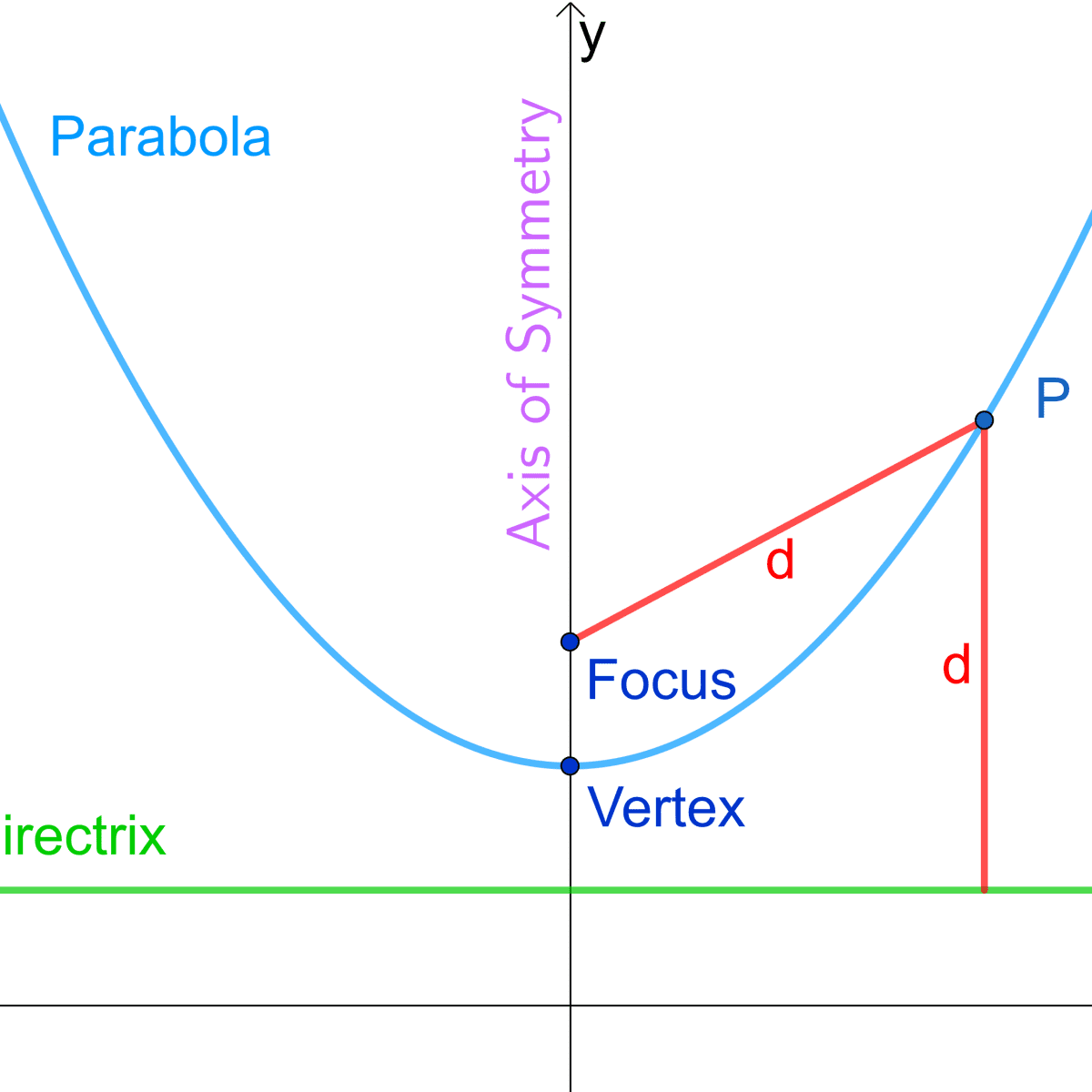
73 Parabolas We have already learned that the graph of a quadratic function f ( x) = a x 2 b x c with a ≠ 0 is called a parabola To our surprise and delight, we may also define parabolas in terms of distance Let F be a point in the plane and D be a line not containing F(xh)^2 = 4p (yk) (0h)^2 = 4p (yk) h^2 = 4p (yk) h^2/4p = ykQuestion Please explain why the graph of (xh)^2 = 4p (yk) has a yintercept of (0, h^2/4p K) Thanks Answer by Nate (3500) ( Show Source ) You can put this solution on YOUR website!




Parabolas
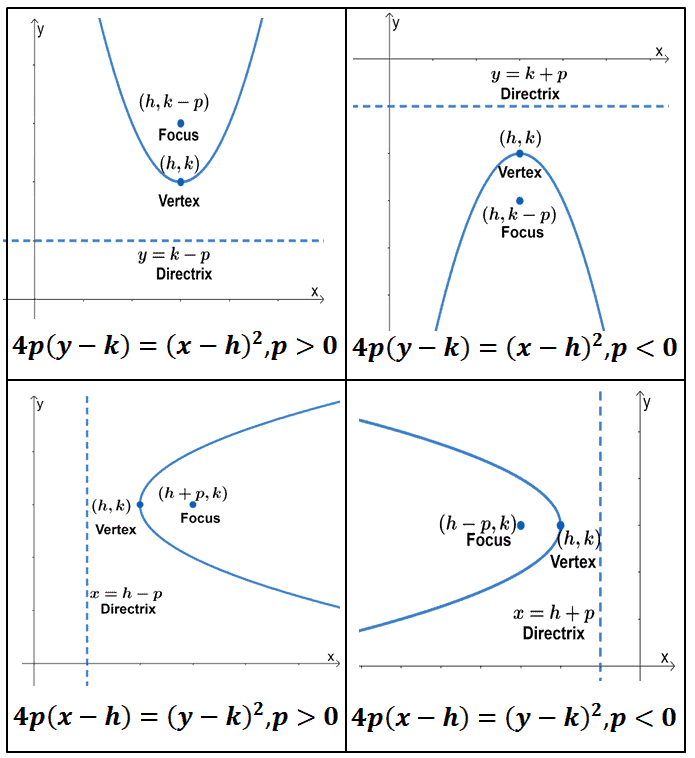



Parabola Properties Components And Graph
The standard form that applies to the given equation is latex{\left(xh\right)}^{2}=4p\left(yk\right)/latex Thus, the axis of symmetry is parallel to the y axis To express the equation of the parabola in this form, we begin by isolating the terms that contain the variable latexx/latex in order to complete the squareSideways x = a(y – k)2 h Copyright © Elizabeth Stapel 1011 All Rights Reserved The conics form of the parabola equation (the one you'll find in advanced or older texts) is regular 4p(y – k) = (x – h)2 sideways 4p(x – h) = (y – k)2(yk) 2 =4p(xh) If we take the equation ( x h) 2 =4p( y k) and expand it we get x 2 2h x h 2 =4p y 4pk or x 2 2h x 4p y 4pkh 2 =0 which is an equation of the form x 2 A x B y C=0, where A, B and C are constants



Solution Find An Equation In Standard Form Of The Parabola Described Vertex At 3 3 Passes Through 0 0 Standard Form Y K 2 4p X H
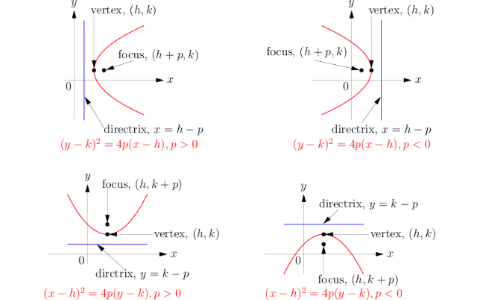



Parabola By Monica Gil On Prezi Next




Conicfm Space Geometric Shapes



Parabolas




Chapter 8 1 Conic Sections Parabolas Honors Pre Calculus Rogers High School Pdf Free Download




Parabolas With Vertex At H K Ck 12 Foundation



Conic Section Parabola 4p Form Geogebra




Solved For The Equation Of The Parabola Given In The Form Chegg Com




Focus Of A Parabola
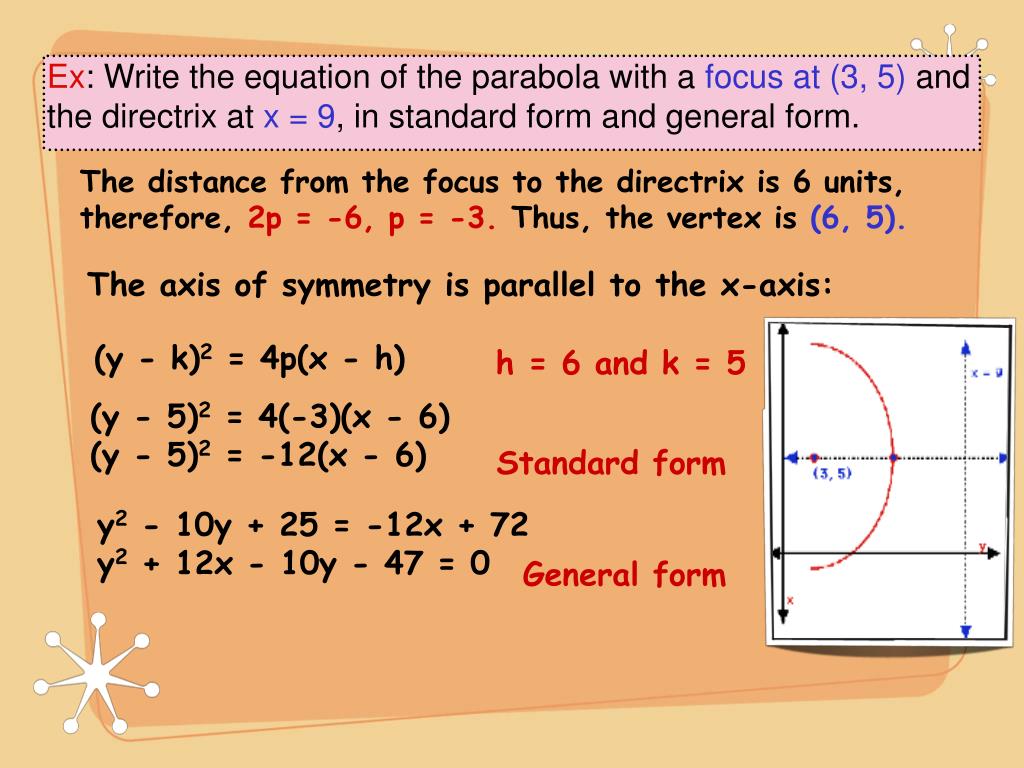



Ppt Parabola Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Equation Of Parabola Directrix Focus Axis Problems With Solutions



2




Parabolas



Http Home Miracosta Edu Dbonds Math 155 lecture notes section 10 1 Pdf



Q Tbn And9gcqk5zl Kvrxykmj8s8e0zjwfnkhta2g2ylbtqgxff1xbalflbml Usqp Cau
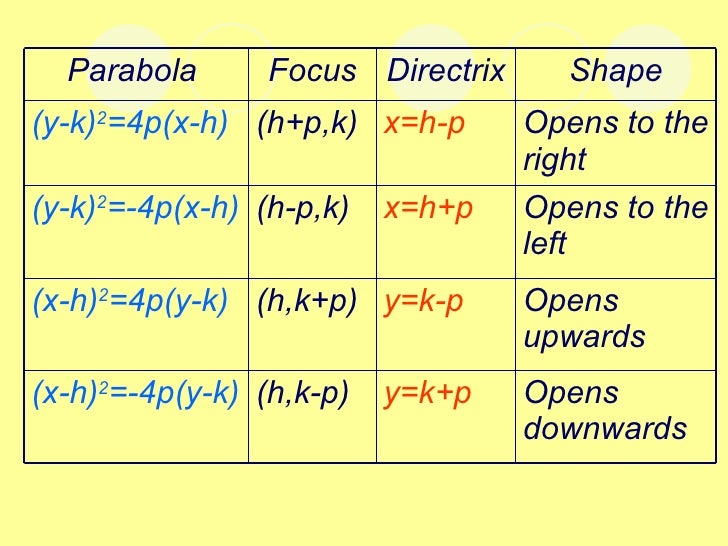



Math1 2



Cochranmath Copy Of Parabola




10 1 Parabolas Ameenaarchives



The Center Of The Circle Is The Vertex Of The Parabola Y 24x 12y 132 0 If The The Circle Intersects The Parabolas Directrix At A Point Where Y 11 What Would Be The Equation Of The
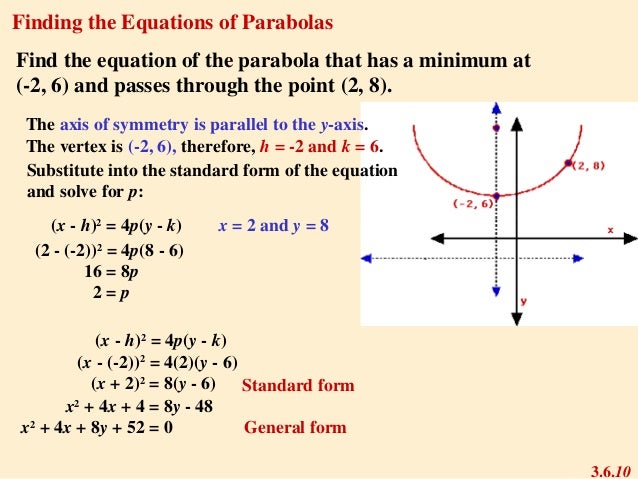



1576 Parabola
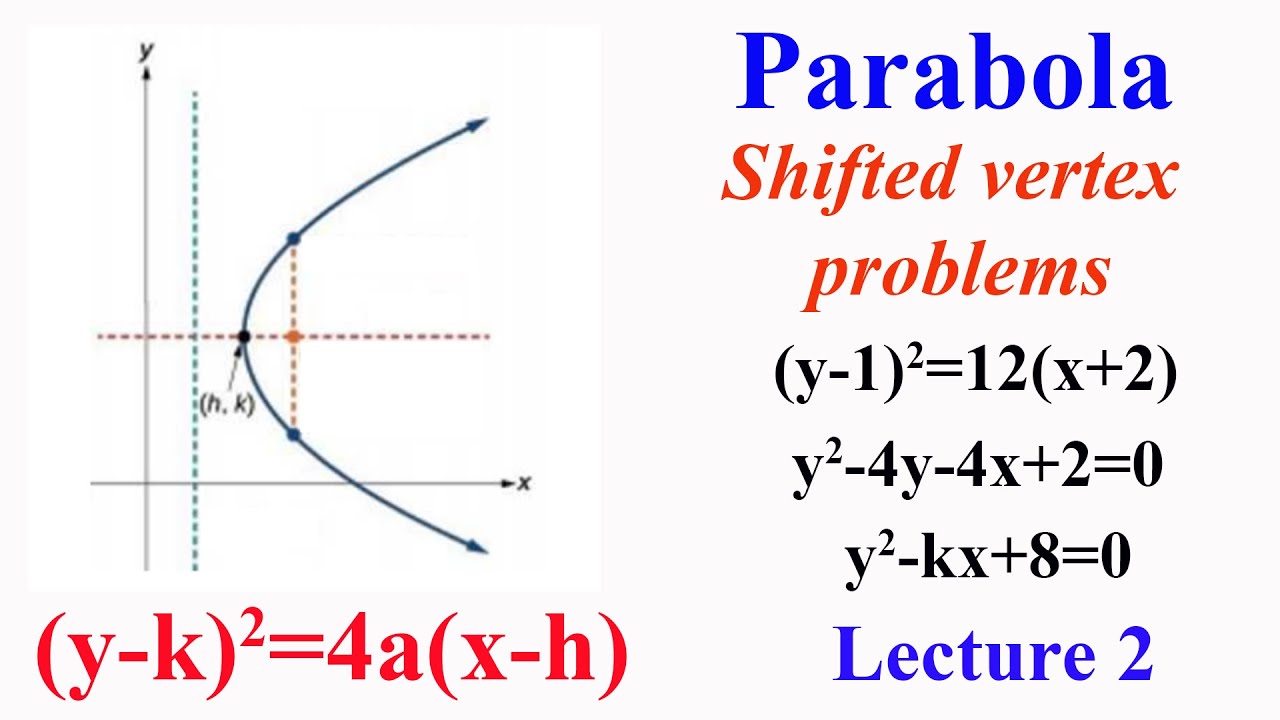



Parabola Lecture 2 Shifted Vertex Y K 2 4a X H With Examples Youtube



Conic Sections Parabolas Summary Analysis Sparknotes
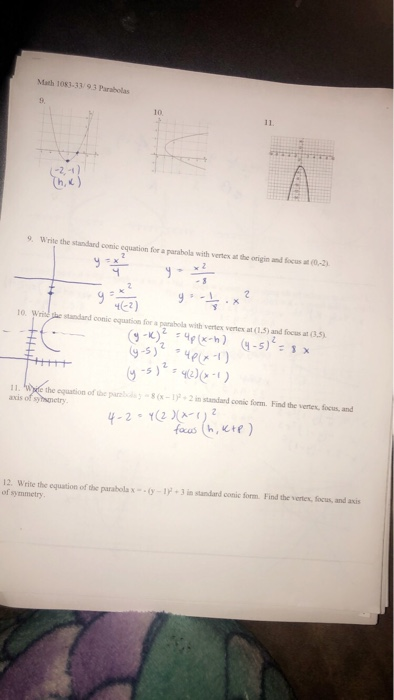



The Directions For 9 11 Is To Write An Equation For Chegg Com



Solution Find The Standard Equation With Focus 2 0 And Directrix X 4 Y K 2 4p X H This Is As Far As I Have Gotten I Think That The Vertex Is 1 0
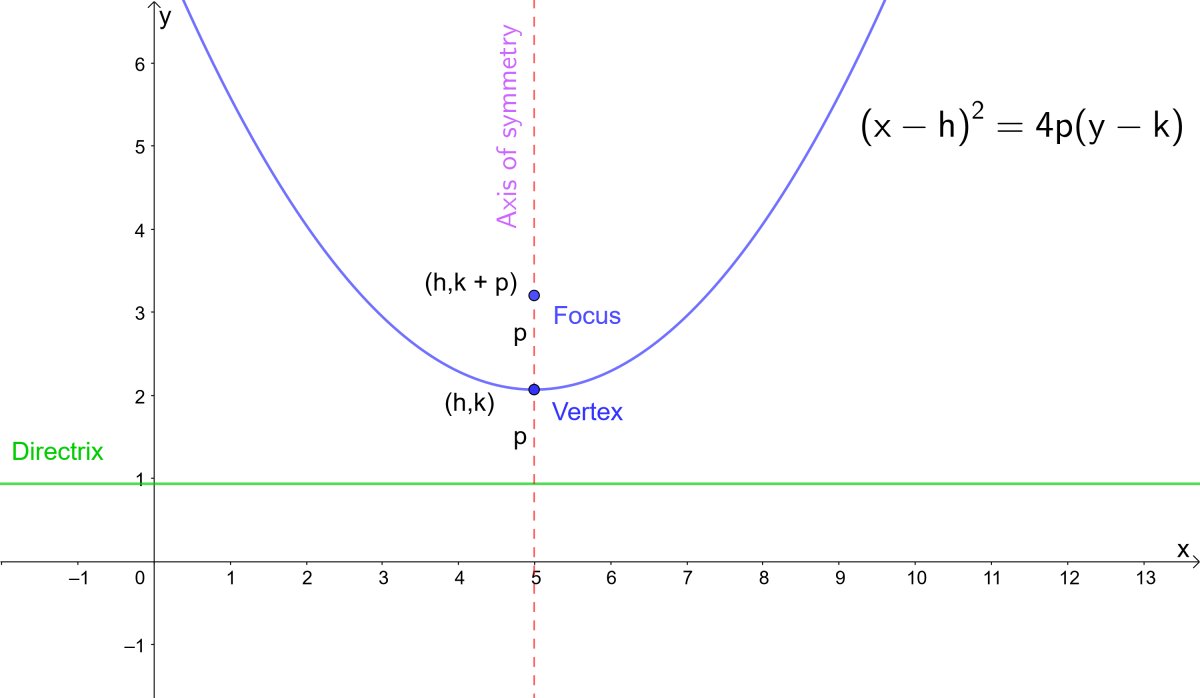



Parabola Equations And Graphs Directrix And Focus And How To Find Roots Of Quadratic Equations Owlcation




For The Equation Of The Parabola Given In The Form Chegg Com



Solution Y 4 2 16 X 1 Which Conic Section Does The Equation Describe



To Graph A Parabola We Need To Know The Coordinates Of Its Vertex Focus And The Equation Of Its Axis
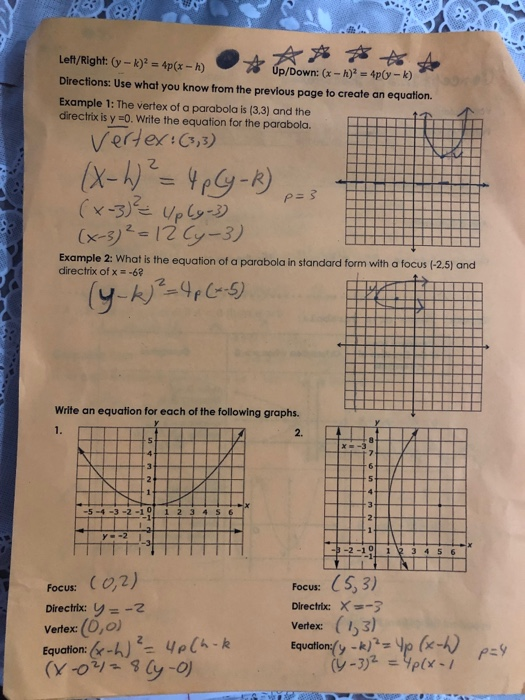



Left Right Y K 2 4p X H Directions Use What You Chegg Com



Conic Section Formula Sheet With Parabola Ellipse And Hyperbola Docsity
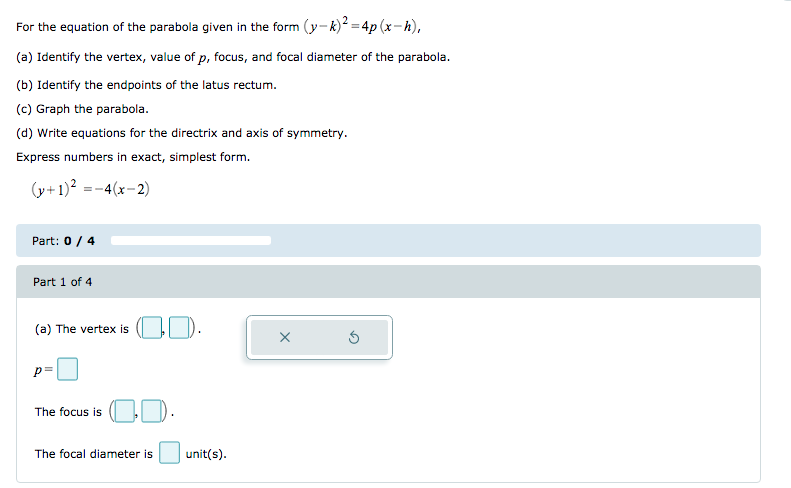



Solved For The Equation Of The Parabola Given In The Form Chegg Com



Ppt Parabola Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Parabolas Andymath Com



Pslv Conic Section



Q Tbn And9gcsrilrja2shkwxd1 Txmt0toiuavnh4boixevpxaxqutk Yqqak Usqp Cau




Lesson 5 1 Parabolas Chart Parabolas With Vertex H K Vertical H K Horizontal H K X H 2 4p Y K Y K 2 4p X H 1 X H 2 4 Opens Upward If P 0 P Course Hero
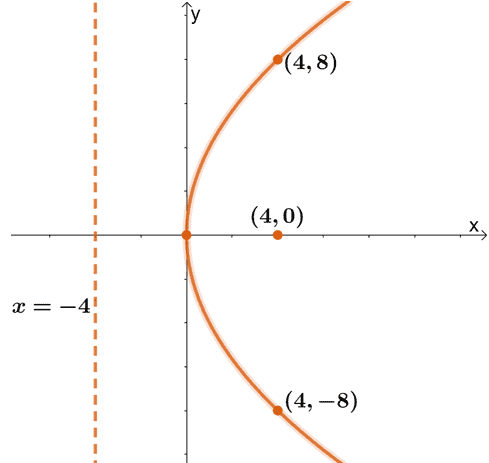



Parabola Properties Components And Graph




Parabolas Con Vertice En H K Ck 12 Foundation
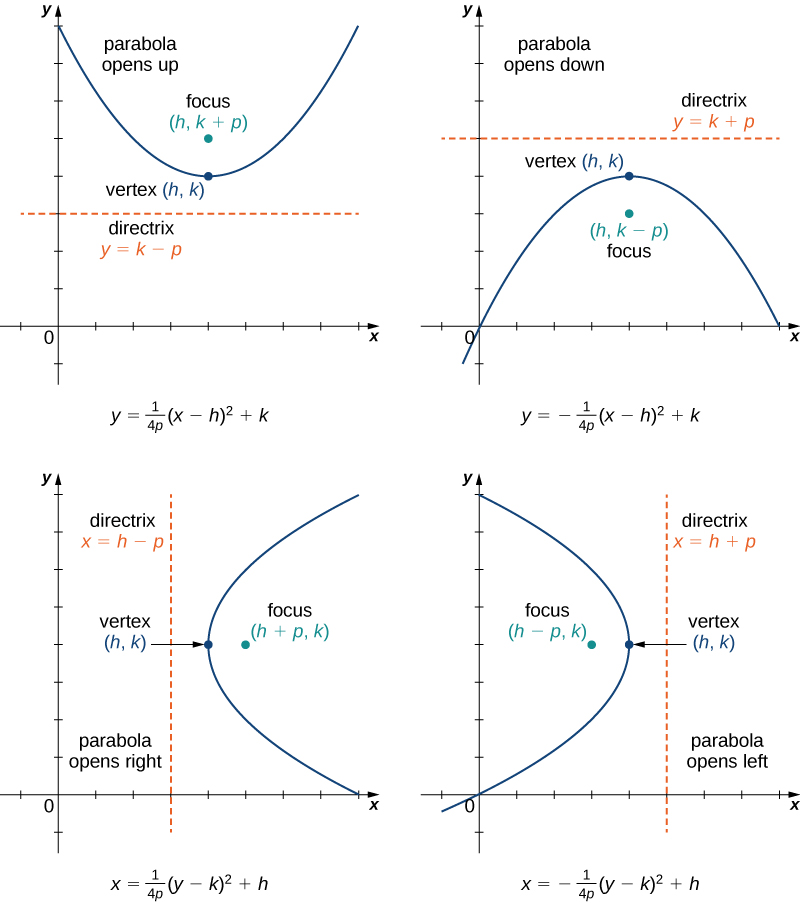



Conic Sections Calculus Volume 2
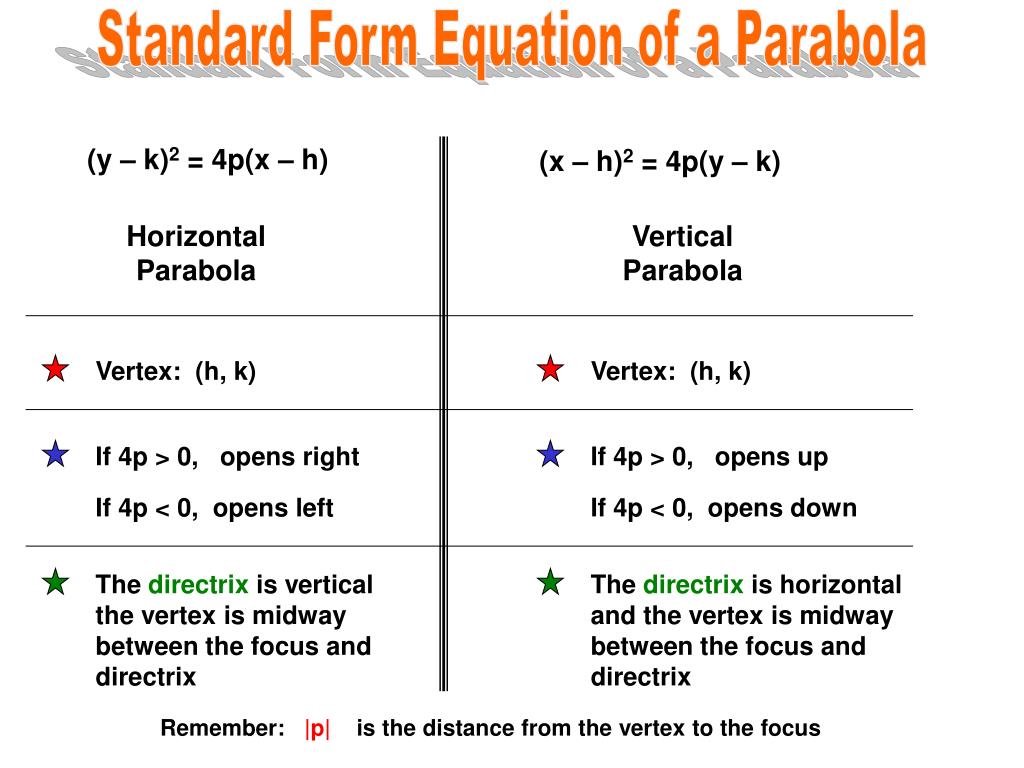



Ppt Math 143 Section 7 3 Parabolas Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
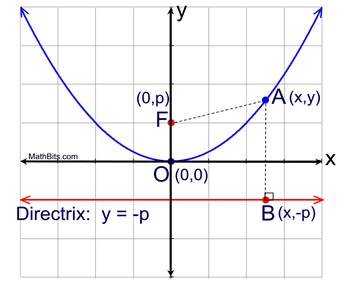



Parabola Equations Mathbitsnotebook Geo Ccss Math



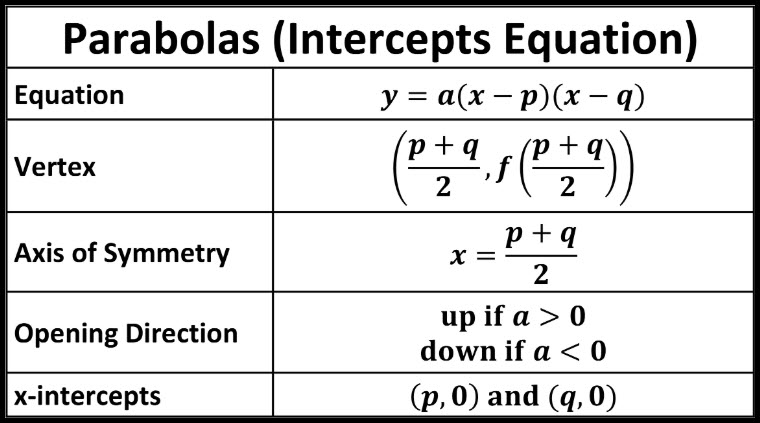
Parabolas Andymath Com



Parabola Conic Sections




Parabola Conic Section Warmup Graph The Following Parabola



Parabolas



Parabolas



Conic Sections Conic Form Of A Parabola
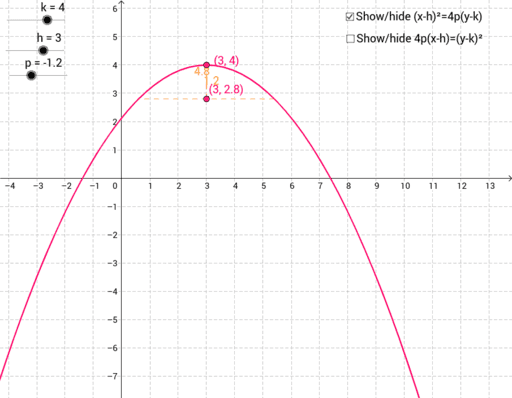



Access Parabola Equation Geogebra




X H 2 4p Y K Y K 2 4p X H If The X Value Is Greater Than 1 The Parabola Will Open Up If The X Value Is Less Than 1 The Parabola Will Open Ppt Download




Equation Of Parabola Directrix Focus Axis Problems With Solutions




What Are The Formula Of Parabola Brainly Ph




X H 2 4p Y K Y K 2 4p X H If The X Value Is Greater Than 1 The Parabola Will Open Up If The X Value Is Less Than 1 The Parabola Will Open Ppt Download



Http Www Lonestar Edu Departments Learningcenter Conicsections Pdf



Parabolas Andymath Com




Parabolas Parabolas




Parabola Conic Section Warmup Graph The Following Parabola



Chapter 10 Analytic Geometry Section 10 1 Parabolas Flip Ebook Pages 1 9 Anyflip Anyflip



Parabolas
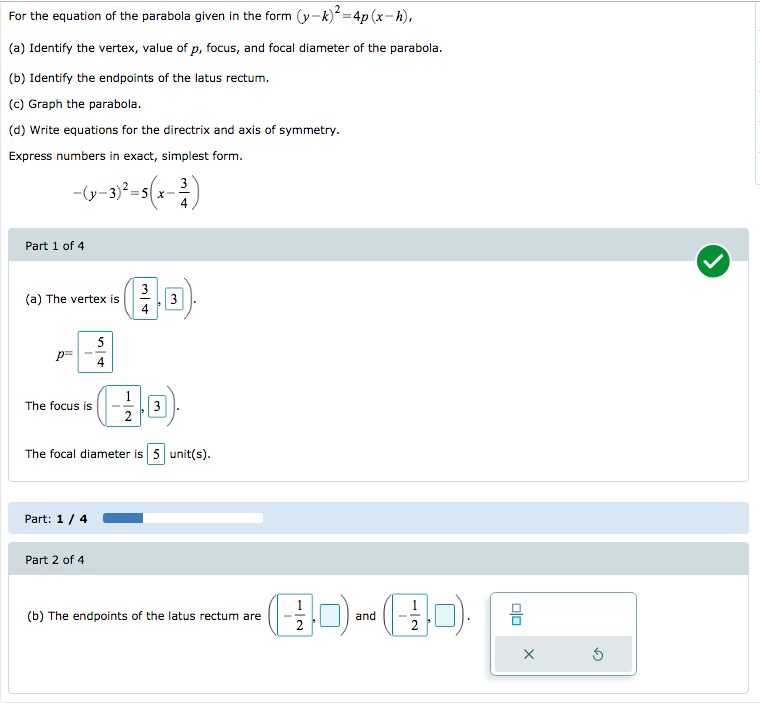



For The Equation Of The Parabola Given In The Form Y Chegg Com



Melissa S Math Analysis Journey Rwa 1 Unit M Concepts 4 6 Conic Sections In Real Life Parabola



Lesson 4 Parabolas In This Lesson Students Will Become Familiar With The Equations And Graphs Of Parabolas The Definition Of A Parabola Will Be Learned Both Algebraically And Using The Distance Relationship Students Will Learn How To Construct A Parabola
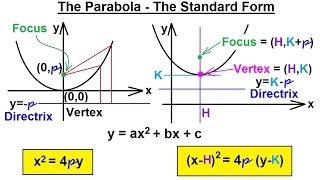



Precalculus Algebra Review Conic Sections 5 Of 27 The Parabola Standard Form Youtube



1



Www Kentschools Net Wp Content Blogs Dir 130 Files 17 04 9 1 New Pdf



2
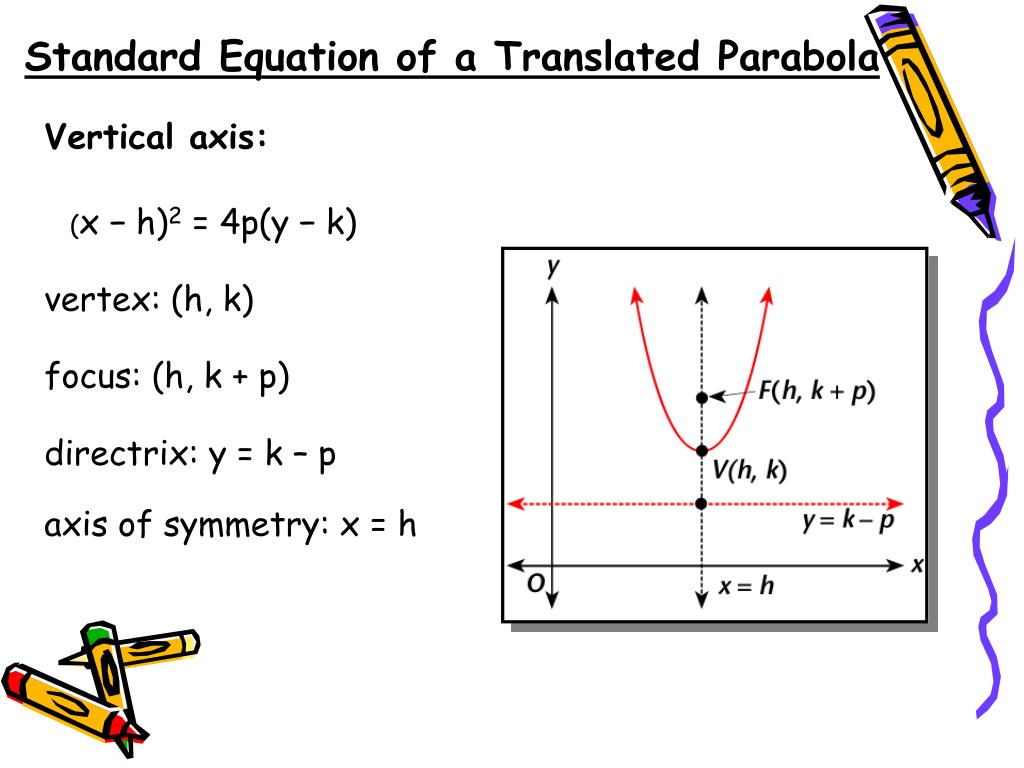



Ppt 8 2 Graph And Write Equations Of Parabolas Powerpoint Presentation Id
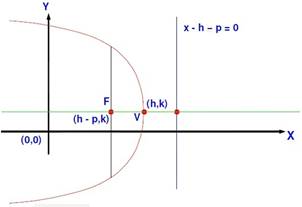



Ecuacion De La Parabola 2




Today In Precalculus Go Over Homework Notes Parabolas With Vertex Other Than 0 0 Homework Ppt Download



Pslv Conic Section




Unit 2 Algebra 2 With Mikhail
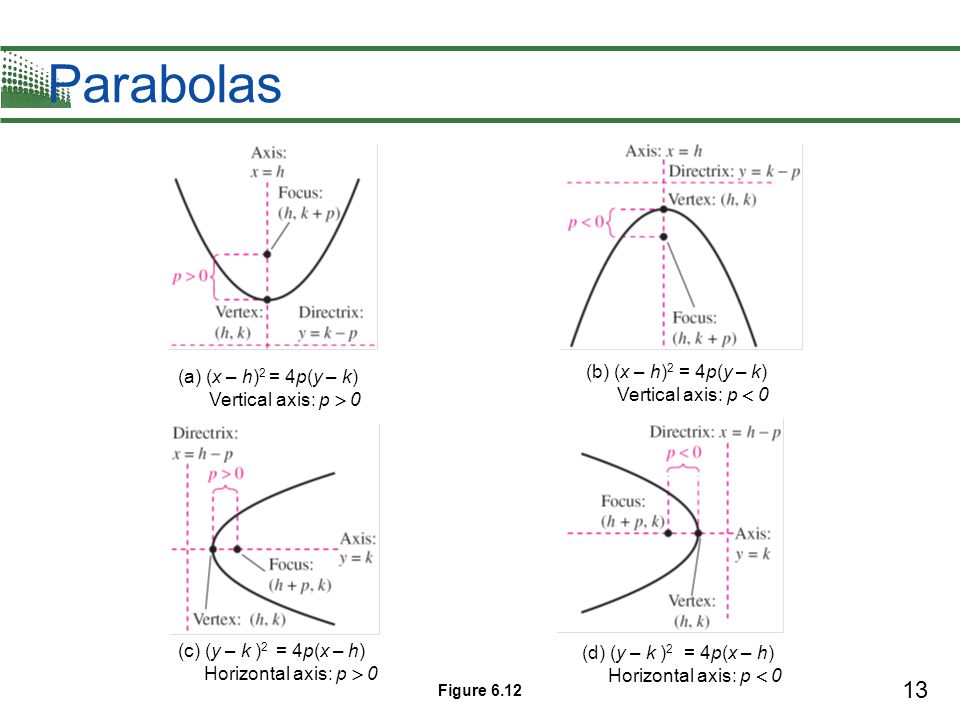



Copyright C Cengage Learning All Rights Reserved Ppt Video Online Download




The Young Math Analysis 101 Rwa 1 Unit M Concept 4 6 Conic Sections In Real Life Scenarios



Www Kentschools Net Wp Content Blogs Dir 130 Files 17 04 9 1 New Pdf




Parabola Conic Section Warmup Graph The Following Parabola




Math Test Conic Sections Flashcards Quizlet
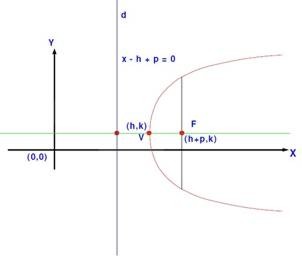



Ecuacion De La Parabola 2



Parabola Equations And Graphs Directrix And Focus And How To Find Roots Of Quadratic Equations Owlcation



Every Day I M Calculatin Rwa1 Unit M Concepts 4 6 Conic Sections In Real Life


